This algorithm returns the diffuse attenuation coefficient for downwelling irradiance at 490 nm ($Kd\_490$) in m-1, calculated using an empirical relationship derived from in situ measurements of $Kd\_490$ and blue-to-green band ratios of remote sensing reflectances (Rrs).
Implementation of this algorithm is contingent on the availability of Rrs in the blue-green spectral region (e.g., 490 - 565 nm). CZCS, OCTS, MODIS-Aqua and -Terra, MERIS, SeaWiFS, VIIRS, and others are all supported.
For PACE OCI, an updated $Kd$ algorithm is used, and it is described here.

Algorithm Point of Contact: P. Jeremy Werdell, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
$R_{rs}$ near 490 nm and between 547 and 565 nm
$Kd\_490$, diffuse attenuation coefficient of downwelling irradiance at 490 nm in m-1
The algorithm is a fourth-order polynomial relationship between a ratio of $R_{rs}$ and $Kd\_490$:
$$ log_{10}\left(K_{bio}\left(490 \right ) \right )=a_0 + \sum_{i=1}^{4}a_i\left(log_{10}\left(\frac{R_{rs}\lambda_{blue}}{R_{rs}\lambda_{green}}\right) \right )^{i} $$
$$ Kd\_490=K_{bio}\left(490\right) + 0.0166 $$
the coefficients for which are sensor-specific:
| sensor | blue | green | a0 | a1 | a2 | a3 | a4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KD2S | SeaWiFS | 490 | 555 | -0.8515 | -1.8263 | 1.8714 | -2.4414 | -1.0690 |
| KD2M | MODIS | 488 | 547 | -0.8813 | -2.0584 | 2.5878 | -3.4885 | -1.5061 |
| KD2E | MERIS | 490 | 560 | -0.8641 | -1.6549 | 2.0112 | -2.5174 | -1.1035 |
| KD2V | VIIRS | 490 | 550 | -0.8730 | -1.8912 | 1.8021 | -2.3865 | -1.0453 |
| KD2O | OCTS | 490 | 565 | -0.8878 | -1.5135 | 2.1459 | -2.4943 | -1.1043 |
| KD2C | CZCS | 443 | 520 | -1.1358 | -2.1146 | 1.6474 | -1.1428 | -0.6190 |
| KD2L | OLI/Landsat 8 | 482 | 561 | -0.9054 | -1.5245 | 2.2392 | -2.4777 | -1.1099 |
The coefficients were derived using version 2 of the NASA bio-Optical Marine Algorithm Data set (NOMAD).
Click get_Kd.c to view source code.
- l2prod = Kd_490
- each satellite will use its sensor-specific coefficients and wavelengths (e.g., SeaWiFS defaults to
KD2S)
- to override the coefficients: kd2_coef = [a0,a1,a2,a3,a4]
- to override the wavelengths: kd2_wave = [numerator wavelength, denominator wavelength]
Satellite-to-in-situ validation results are available from the SeaWiFS Bio-Optical Archive and Storage System (SeaBASS):
| KD2S | KD2M | KD2E |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| KD2V | KD2O | KD2C |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
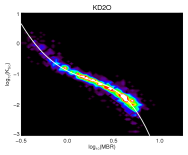 |
 |


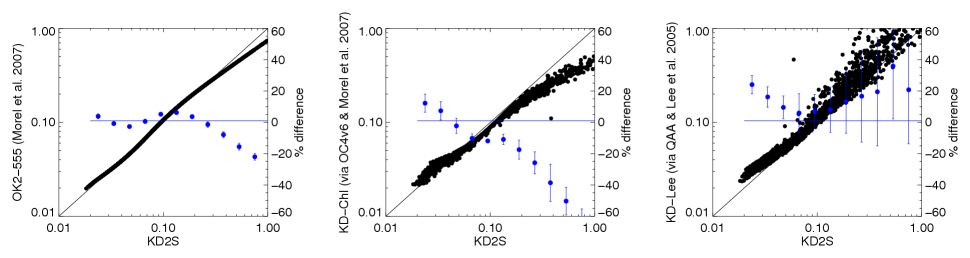
KD2S is compared with (Morel et al. 2007) (both Rrs- and Chl-driven) and (Lee 2005)
Austin, R. W., & Petzold, T. J. (1981). The determination of the diffuse attenuation coefficient of sea water using the Coastal Zone Color Scanner. In: J.F.R. Gower, Ed., Oceanography from Space, Plenum Press, New York, 239-256, http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-3315-9_29
Lee, Z.-P. (2005). A model for the diffuse attenuation coefficient of downwelling irradiance. Journal of Geophysical Research, 110(C2). http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2004jc002275
Morel, A., Huot, Y., Gentili, B., Werdell, P. J., Hooker, S. B., & Franz, B. A. (2007). Examining the consistency of products derived from various ocean color sensors in open ocean (Case 1) waters in the perspective of a multi-sensor approach. Remote Sensing of Environment, 111(1), 69-88. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2007.03.012
O'Reilly, J.E. & 24 co-authors (2000). SeaWiFS Postlaunch Calibration and Validation Analyses, Part 3. NASA Tech. Memo. 2000-206892, Vol. 11, S.B. Hooker and E.R. Firestone, Eds., NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, 49 pp.
Yeh, E-N. & 7 co-authors (1997). Case Studies for SeaWiFS Calibration and Validation, Part 4. NASA Tech. Memo. 104566, Vol. 41, S.B. Hooker and E.R. Firestone, Eds., NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, 35 pp.
Werdell, P. J. & Bailey, S. W. (2005). An improved bio-optical data set for ocean color algorithm development and satellite data product validation. Remote Sensing of Environment 98, 122-140, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2005.07.001.